Humanoid Robots + Cryptocurrency: How does Reborn build the DePAI flywheel?
Author: brianbreslow , Hypersphere Ventures
Compiled by: Tim, PANews
Executive Summary
- Humanoid general-purpose robots are rapidly moving from science fiction to reality. Declining hardware costs, growing capital investments, and technological breakthroughs in motion and manipulation are converging to drive the next major platform iteration in computing.
- Although the increasing commoditization of computing power and hardware equipment has brought low-cost advantages to robotics engineering, the industry is still constrained by the bottleneck of training data.
- Reborn is one of the few projects that leverages Decentralized Physical AI (DePAI) to crowdsource high-precision motion and synthetic data and build robotic foundation models, which puts it in a unique position to advance the deployment of humanoid robots. The project is led by a technically sophisticated founding team with academic research and professorships at UC Berkeley, Cornell, Harvard, and Apple, demonstrating both academic excellence and real-world engineering execution.
Humanoid robots: from science fiction to cutting-edge applications
The commercialization of robotics technology is not a new concept. The well-known iRobot Roomba vacuum cleaner launched in 2002, or the Kasa pet camera and other household robots that have emerged in recent years, are all single-function devices. With the development of artificial intelligence, robots are evolving from single-function machines to multi-function forms, designed to adapt to operations in open environments.
In the next 5 to 15 years, humanoid robots will gradually upgrade from basic tasks such as cleaning and cooking, and will eventually be able to perform complex tasks such as reception services, firefighting and even surgical operations.
Recent developments are moving humanoid robots from science fiction to reality.
- Market dynamics: More than 100 companies are planning to develop humanoid robots (such as Tesla, Yushu Technology, Figure AI, Clone, Agile, etc.).
- Hardware technology has successfully crossed the uncanny valley: the new generation of humanoid robots exhibits natural and smooth movements, enabling human-like interactions in real environments. Among them, the walking speed of Yushu H1 can reach 3.3 meters per second, far exceeding the average walking speed of 1.4 meters per second for humans.
(Note: The Uncanny Valley is a psychological theory that describes humans' emotional responses to non-human entities (such as robots, dolls, virtual images, etc.).
- New paradigm in humanoid robot costs: expected to be lower than U.S. labor wages by 2032.
Development bottleneck: real-world training data
Despite the clear positive factors in the field of humanoid robots, poor data quality and scarcity continue to hinder their large-scale deployment.
Other AI entities, such as autonomous driving, have largely solved the data problem through cameras and sensors installed in existing vehicles. Take Tesla, Waymo and other autonomous driving systems as examples. These fleets are able to generate billions of miles of real-world road driving data. When Waymo puts its vehicles on the road at this stage of development, it has a real person in the passenger seat for real-time training.
However, consumers are unlikely to accept the existence of a "robot nanny". Robots must have high performance out of the box, which makes data collection before deployment essential. All training must be completed before commercial production, and the scale and quality of data remain persistent challenges.
While each training model has its own scale unit (e.g. tokens for large language models, video-text pairs for image generators, motion clips for robotics), the comparison below clearly reveals the order of magnitude gap in data availability for robotics:
- GPT-4's training data size exceeds 15 trillion text tokens.
- Midjourney and Sora leverage billions of labeled video-text pairs.
- In comparison, the largest robotics dataset contains only about 2.4 million interaction records.
This gap explains why robotics has not yet achieved a true foundational model like large language models, the key is that the data foundation is still incomplete.
Traditional data collection methods are difficult to meet the large-scale requirements of humanoid robot training data. Existing methods include:
- Simulation: low cost but lacks real boundary scenarios (the gap between simulation and reality)
- Internet videos: cannot provide the proprioception and force feedback environment necessary for robot learning
- Real-world data: Although accurate, it requires remote control and human closed-loop operation, which leads to high costs (more than $40,000 per robot) and lack of scalability.
Training models in virtual environments is cheap and scalable, but these models often struggle when deployed in the real world. This problem is known as the Sim2Real gap.
For example, a robot trained in a simulation might be able to easily pick up perfectly lit, smooth objects, but it often struggles with clutter, bumpy textures, or the kinds of unexpected situations that humans take for granted in the real world.
Reborn provides a cost-effective and fast way to crowdsource real-world data to enhance robot training and solve the "Sim2Real gap" problem.
Reborn: A full-stack vision for decentralized entity AI
Reborn is building a vertically integrated software and data platform for embodied intelligent robotic applications. The company's core goal is to solve the data bottleneck problem in the field of humanoid robots, but its vision goes far beyond that. Through the combination of self-developed hardware, multimodal simulation infrastructure and basic models, Reborn will become a full-stack driver for embodied intelligence.
The Reborn platform uses the proprietary consumer-grade motion capture device "ReboCap" as a starting point to build a rapidly expanding augmented reality and virtual reality gaming ecosystem. Users provide high-fidelity motion data in exchange for network incentives and rewards to drive the platform's continued development. Reborn has sold more than 5,000 sets of ReboCap devices, has 160,000 monthly active users, and has established a clear growth path to exceed 2 million users by the end of the year.
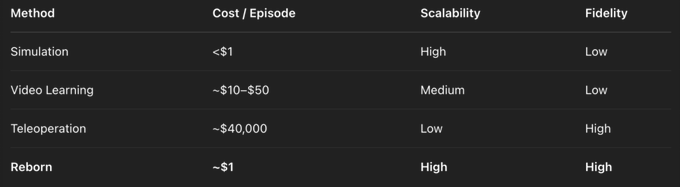
Reborn supports data collection at a much higher efficiency than other solutions.
What is remarkable is that this growth is entirely due to natural development: users are attracted by the entertainment of the game itself, and anchors use ReboCap to achieve real-time body capture of digital images. This spontaneously formed virtuous cycle has achieved scalable, low-cost, and high-fidelity data production, making the Reborn dataset a training resource that top robotics companies are competing to adopt.
The second layer of the ReBorn software stack is Roboverse: a multimodal data platform that unifies fragmented simulation environments. The current simulation field is highly fragmented, with tools such as Mujoco and NVIDIA Isaac Lab operating independently, each with its own advantages but unable to communicate with each other. This fragmentation has slowed down the development process and widened the gap between simulation and reality. Roboverse creates a shared virtual infrastructure for developing and evaluating robot models by standardizing multiple simulators. This integration supports consistent benchmarking, which greatly improves the system's scalability and generalization capabilities.
Roboverse achieves seamless collaboration. The former collects real-world data on a large scale, while the latter builds a simulation environment to drive model training. The two work together to demonstrate the true strength of Reborn's distributed physical intelligence network. The platform is creating a physical artificial intelligence developer ecosystem that goes beyond simple data acquisition, and its functions have extended to the field of actual model deployment and commercial authorization.
Reborn basic model
Perhaps the most critical component of the Reborn technology stack is the Reborn Foundation Model (RFM). As one of the first robotics foundation models, this model is being built as a core system for the emerging physical AI infrastructure. Its positioning is similar to traditional large language foundation models, such as OpenAI's GPT-4 or Meta's Llama, but for the robotics field.
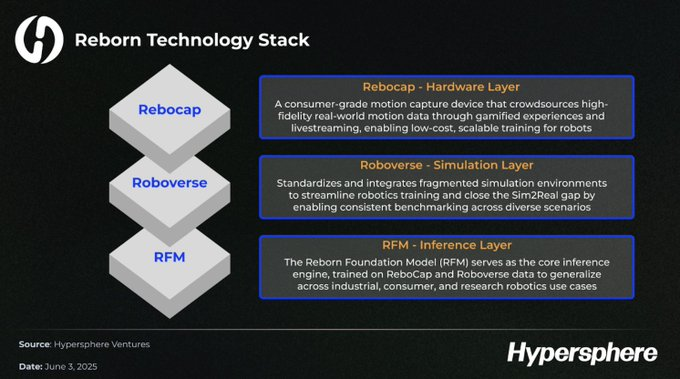
Reborn Technology Stack
The three core components of the Reborn technology stack (ReboCap data platform, Roboverse simulation system and RFM model authorization mechanism) together build a solid vertical integration moat. By combining crowdsourced motion data with a powerful simulation system and model authorization system, Reborn is able to train a basic model with cross-scenario generalization capabilities. This model can support a variety of robot applications in the industrial, consumer and research fields, and achieve universal deployment under massive and diverse data.
Reborn is actively advancing the commercialization of its technology, launching paid pilot projects with Galbot and Noematrix, and establishing strategic partnerships with Unitree, Booster Robotics, Swiss Mile, and Agile Robots. China's humanoid robot market is experiencing rapid growth, accounting for about 32.7% of the global market. Notably, Yushu Technology accounts for more than 60% of the global quadruped robot market and is one of the six Chinese manufacturers that plan to produce more than 1,000 units by 2025.
The Role of Cryptocurrency in the Physical AI Technology Stack
Crypto is building a complete vertical stack for physical world AI.
Reborn is the leading embodied AI cryptocurrency project
Although these projects belong to different levels of the physical artificial intelligence stack, they have one thing in common: they are all 100% DePAI projects. DePAI uses token incentives throughout the entire technology stack to create an open, composable, and permissionless expansion mechanism. It is this innovation that makes the decentralized development of physical artificial intelligence a reality.
Reborn has not yet issued tokens, and the organic growth of its business is even more valuable. When the token incentive mechanism is officially launched, network participation will be accelerated as a key link in the DePAI flywheel effect: users who purchase Reborn hardware devices (ReboCap collectors) can receive incentives from the project, and robot R&D companies will pay contribution rewards to ReboCap holders. This dual incentive will encourage more people to purchase and use ReboCap devices. At the same time, the project will dynamically incentivize the collection of high-value customized behavioral data, thereby more effectively bridging the technical gap between simulation and real-world applications (Sim2Real).
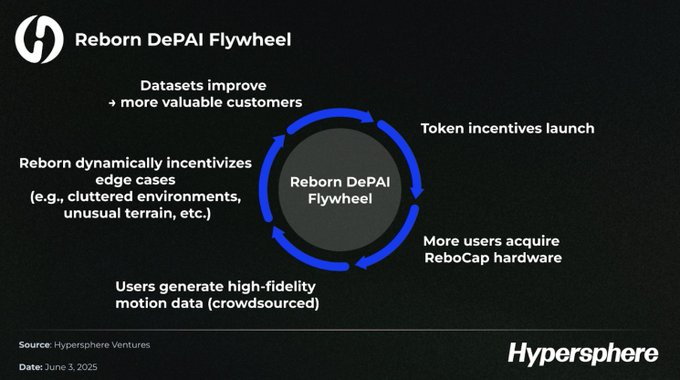
Reborn's DePAI flywheel is in motion
The "ChatGPT moment" in the field of robotics will not be triggered by robotics companies themselves, because hardware deployment is far more complex than software. The explosive growth of robotics technology is naturally limited by cost, hardware availability and deployment complexity, and these obstacles do not exist at all in pure digital software such as ChatGPT.
The turning point for humanoid robots is not how amazing the prototype is, but when the cost drops to a level that is affordable to the public, just like the popularity of smartphones or computers. When the cost drops, hardware will become just an entry ticket, and the real competitive advantage lies in data and models: specifically, the scale, quality, and diversity of the motor intelligence used to train the machine.
Conclusion
The robotics platform revolution is unstoppable, but like all platforms, its scalable development cannot be separated from data support. As a high-leverage bet, Reborn firmly believes that crypto technology can fill the most critical gap in the AI robotics technology stack: its robotics data solution DePAI is cost-effective, highly scalable and modular. When robotics technology becomes the next frontier of AI, Reborn is turning the general public into "miners" of motion data. Just as large language models require text tagging support, humanoid robots require massive motion sequence training. With Reborn, we will break through the last bottleneck and realize the leap of humanoid robots from science fiction to reality.
You May Also Like

Liquidity Wars 3.0: Bribery Becomes a Market

Inside the IRS’s Expanding Surveillance of Crypto Investors
